

There are about two dozen sympathetic chains present close to the spinal cord. Norepinephrine is the main neurotransmitter present in the sympathetic nervous system. This is called exocytosis.Īlso Read: Differences between Endocytosis and Exocytosis It normally happens when any action causes the vesicles to release their contents directly to the synaptic cleft. Norepinephrine is accumulated in these vesicles until it is ejected into the synaptic cleft. Reserpine is a counter for VMAT as it inhibits the process. The transfer of norepinephrine from the cytosol to synaptic vesicles is done by vesicular monoamine transporter(VMAT). There are a fixed set of mechanisms common to monoamine neurotransmitters. It acts as a neurotransmitter inside the brain. There are two types of alpha receptors- α1 and α2. Norepinephrine has been classified into two major categories - alpha and beta-adrenergic.
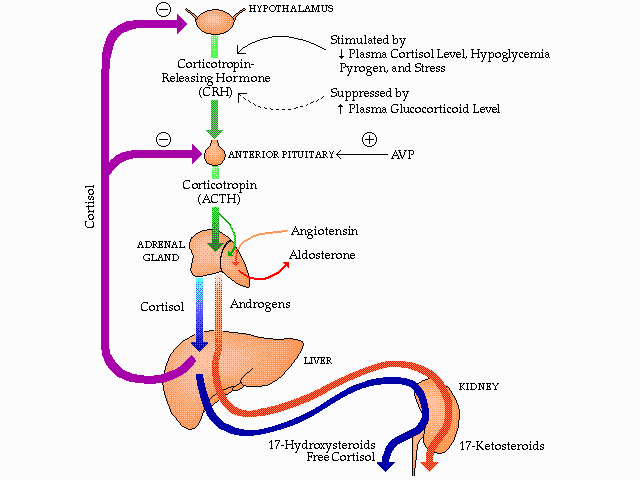
Similar to other hormones, norepinephrine works after binding to the active receptors present on the cells. The main functions of the Norepinephrine hormone are stated below: Increased alertness, pupillary dilation, piloerection (raising of hairs), sweating etc are all due to Norepinephrine and it also increases the heartbeat by strengthening heart contraction and the rate of respiration.
It is secreted rapidly in response to the stress of any kind and during emergency situations and is thus called emergency hormones or hormones of Fight or Flight. Norepinephrine which is also known as noradrenaline is a hormone released by the Adrenal Medulla along with adrenaline or epinephrine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
